United Airlines Flight UA770 experienced multiple emergency diversions throughout 2025, highlighting the critical importance of aviation safety protocols and crew preparedness. These incidents involved different routes and aircraft types, demonstrating how modern aviation handles technical alerts and potential system malfunctions through precautionary measures designed to protect passenger safety.
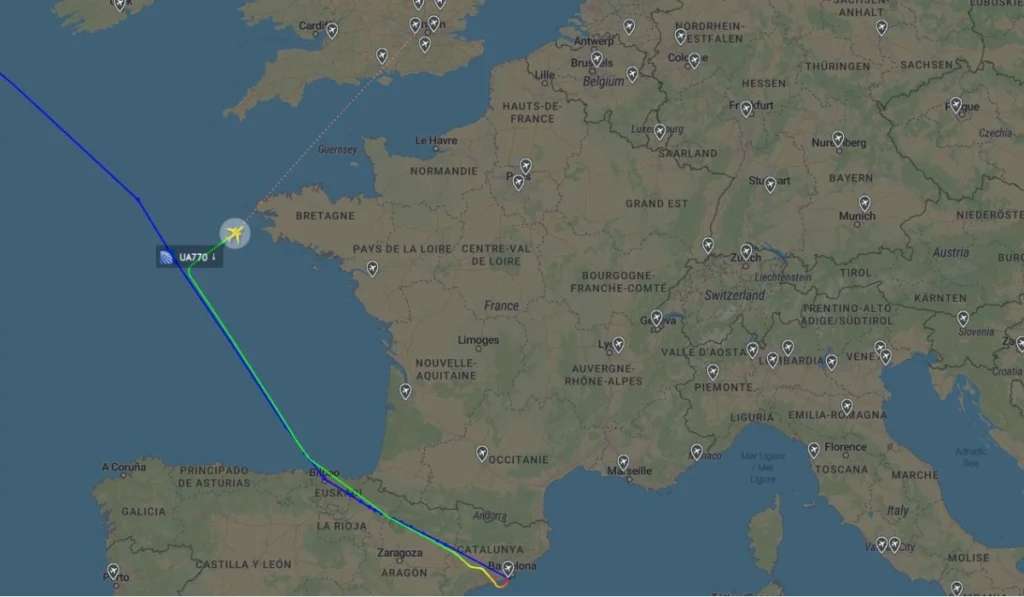
The first notable incident occurred on May 27, 2025, when Flight UA770 operating from Barcelona to Chicago O’Hare aboard a Boeing seven eight seven dash nine Dreamliner declared a general emergency mid-flight. The aircraft, bearing registration N two six nine zero two, was cruising over the North Atlantic when the cockpit received alerts related to cabin pressurization systems. The pilots squawked seven seven zero zero, the international aviation code signaling a general emergency, which immediately gave the aircraft top priority with air traffic controllers and triggered emergency protocols across affected airspace.
The flight crew coordinated with air traffic control and diverted to London Heathrow Airport, one of Europe’s most prepared facilities for handling emergency aircraft landings. The aircraft landed at approximately four fifty five PM BST on Runway two seven R, a standard choice for heavy aircraft at Heathrow. All two hundred fifty seven passengers and twelve crew members remained unharmed, with no cabin decompression occurring despite the pressurization system warnings. Emergency vehicles positioned themselves before touchdown as standard precautionary procedure, though the landing proceeded without incident.
Cabin pressurization alerts represent serious concerns for transatlantic flights operating at altitudes exceeding thirty five thousand feet. Modern aircraft like the Boeing seven eight seven Dreamliner maintain cabin pressure equivalent to approximately six thousand to eight thousand feet above sea level even when flying at cruising altitude. Any anomaly in these systems requires immediate attention because pressurization failures can escalate quickly at high altitudes. The flight crew’s decision to divert rather than continue across the Atlantic demonstrated adherence to conservative safety protocols prioritizing passenger welfare over schedule convenience.
Passengers aboard the May incident reported calm and professional handling by the flight crew. Flight attendants moved quickly and professionally to calm any nervous passengers, with no panic ensuing, which aviation experts attributed to efficient crew communication and experienced staff. The captain announced the technical irregularity and explained the precautionary landing in Denver, keeping passengers informed throughout the diversion process. Oxygen masks did not deploy, confirming that cabin pressure remained stable despite the system alerts.
Another emergency diversion involving Flight UA770 occurred on July twenty eight, two thousand twenty five, when the flight traveling from San Francisco to Chicago detected unusual indicators related to critical aircraft systems approximately ninety minutes into the journey. The captain declared an emergency and rerouted the aircraft to Denver International Airport, the closest major facility with advanced emergency infrastructure. The warning signals did not confirm actual system failure, but aviation protocols require treating any anomalies in critical systems with maximum caution to prevent potential escalation.
United Airlines issued a public statement within hours confirming the diversion occurred “out of an abundance of caution due to an onboard sensor alert”. The airline emphasized that safety remained their top priority and that thorough maintenance inspection of the aircraft would be completed before returning to service. Modern aircraft contain hundreds of sensors monitoring everything from cabin pressure and temperature to engine performance and hydraulic systems, making it challenging to determine which specific sensor triggered the diversion without detailed technical analysis.
A third incident occurred on August fourteen, two thousand twenty five, when Flight UA770 departed Los Angeles International Airport at four twelve PM local time bound for Chicago O’Hare. Approximately halfway through the flight, the captain announced a technical irregularity and informed passengers they would be landing in Denver as a precaution. This particular aircraft was identified as a Boeing seven three seven MAX nine, which prompted some observers to recall past issues with the MAX series. However, the Federal Aviation Administration confirmed this specific aircraft had passed all recent inspections and did not fall under any temporary grounding orders.
Aircraft maintenance records showed no red flags in the days leading up to the August flight, according to data indicating the plane was delivered to United in late two thousand twenty three and had logged under two thousand flight hours. Boeing and United maintenance teams initiated joint post-incident reviews to inspect the aircraft thoroughly after each diversion. The Federal Aviation Administration requested post-flight reports from United for each incident, though it does not automatically investigate every diversion unless patterns emerge suggesting systemic issues.
The multiple UA770 diversions throughout two thousand twenty five raised questions about transparency and communication in aviation incidents. Social media platforms filled with hashtag UA seven seven zero posts from passengers expressing both gratitude for safe landings and frustration about missed connections and vague updates. Some travelers questioned whether airlines provide sufficient detail about technical issues prompting diversions, while others appreciated the conservative approach prioritizing safety over schedule adherence.
Upon landing at diversion airports, passengers received assistance from gate agents and medical staff, though no one required medical treatment in any of the incidents. United Airlines provided meal vouchers, rebooking on alternative flights, and overnight accommodations when necessary. The airline’s response demonstrated standard protocols for handling emergency diversions, ensuring passengers reached their final destinations despite delays and disruptions to travel plans.
Aviation safety experts emphasized that emergency diversions, while unsettling for passengers, represent exactly how modern aviation safety systems should function. Aircraft warning systems detect potential issues early, allowing flight crews to respond before situations become critical. The decision to divert reflects conservative risk management rather than indicating imminent danger. Pilots receive rigorous training in emergency procedures and decision-making, preparing them to handle unexpected situations with calm professionalism.
The choice of diversion airports in these incidents reflected strategic considerations including proximity to the flight path, availability of appropriate runway length and emergency services, and capability to handle specific aircraft types. Denver International Airport serves as a common diversion point for flights between West Coast and Midwest destinations due to its central location and comprehensive facilities. London Heathrow’s selection for the Barcelona to Chicago flight reflected its position along transatlantic routes and exceptional emergency response capabilities.
Modern commercial aviation maintains layered safety systems ensuring multiple redundancies for critical functions. Environmental control systems, including pressurization, feature backup components allowing continued safe operation even if primary systems experience issues. Cockpit alerts notify crews of anomalies before they develop into emergencies, providing time for appropriate responses. This redundancy philosophy means that warning signals often indicate potential problems rather than actual failures, explaining why diverted aircraft frequently undergo inspection without revealing major malfunctions.
Passenger experiences during emergency diversions vary depending on individual temperaments and crew communication effectiveness. Travelers aboard UA770 incidents reported ranging from minimal concern to significant anxiety, with most praising flight attendant professionalism in maintaining calm cabin environments. Clear announcements explaining situations without excessive technical detail help passengers understand circumstances without causing unnecessary alarm. Crew training emphasizes balancing transparency with reassurance, providing information while maintaining confidence in the aircraft’s safety.
The frequency of emergency diversions has increased slightly in recent years due to several factors including increased air travel volumes following the pandemic, more sensitive sensor technologies detecting anomalies earlier, and rising incidents of medical emergencies aboard aircraft. Airlines maintain strict adherence to safety regulations ensuring consistent high standards across the industry when alerts like those experienced by UA770 occur. The philosophy remains clear that safety considerations always take precedence over operational efficiency or schedule maintenance.
Technical investigations following each UA770 diversion examined multiple potential causes including sensor malfunctions, actual system irregularities, and environmental factors affecting aircraft performance. Boeing technical representatives worked alongside United maintenance teams to analyze data from aircraft monitoring systems, identifying root causes and implementing corrective actions. These investigations typically remain confidential unless they reveal issues requiring broader industry notification through airworthiness directives or service bulletins.
The Boeing seven eight seven Dreamliner involved in the Barcelona to Chicago incident represents advanced aviation technology with sophisticated monitoring and control systems. Known for fuel efficiency, passenger comfort, and long-range capability, the Dreamliner has become a workhorse for international routes. The aircraft features composite construction, advanced avionics, and environmental systems designed to maintain optimal cabin conditions during extended flights. Despite its technological sophistication, the Dreamliner, like all aircraft, requires human judgment when warning systems activate.
Passenger compensation and assistance following emergency diversions depends on factors including fare rules, airline policies, and applicable regulations. European Union regulations provide stronger passenger rights for flights departing from or arriving in EU countries, potentially entitling travelers to compensation for significant delays caused by diversions. United Airlines’ standard practice includes rebooking passengers on next available flights and providing necessary accommodations and meals during extended delays. Some passengers opted to continue journeys via alternate carriers when United’s rebooking options proved inconvenient.
The psychological impact of emergency diversions on passengers varies widely. Frequent flyers often take such incidents in stride, understanding that diversions reflect proper safety procedures. Less experienced travelers may find the experience frightening, potentially affecting their comfort with future air travel. Airlines recognize these concerns and train cabin crews in passenger psychology and communication techniques designed to minimize anxiety during irregular operations.
Aviation industry observers noted that the multiple UA770 incidents in two thousand twenty five, while sharing a flight number, involved different aircraft, routes, and technical issues. Flight numbers represent scheduled services rather than specific airplanes, meaning UA770 operates daily with various aircraft depending on demand and aircraft availability. The coincidence of multiple diversions sharing the same flight number attracted media attention but did not indicate systemic problems with a particular aircraft or route.
The incidents reinforced several key lessons for air travelers. Emergency diversions, while disruptive, demonstrate functional safety systems and well-trained crews. Pilots make conservative decisions when faced with technical uncertainties, erring on the side of caution rather than risking continued flight with potential issues. Modern aviation remains one of the safest forms of transportation precisely because of this cautious approach to anomalies and strict adherence to established protocols.
Long-term implications of the UA770 diversions may include updated inspection protocols or maintenance schedules if investigations reveal patterns requiring attention. Airlines continuously refine procedures based on operational experiences, using incidents as learning opportunities to enhance safety further. Boeing may issue technical guidance to operators if specific sensor behaviors or system characteristics warrant attention across the fleet.
The collaborative nature of aviation safety became evident through these incidents. Flight crews, air traffic controllers, airline operations centers, airport emergency services, and maintenance teams all coordinated seamlessly to ensure safe outcomes. This cooperation reflects decades of refinement in aviation safety culture, where information sharing and standardized procedures enable effective responses to unexpected situations regardless of where they occur globally.
Future air travelers can take comfort from how the UA770 diversions were handled. Each incident concluded without injuries, property damage, or lasting consequences beyond schedule disruptions. The professionalism displayed by United crews and the effectiveness of aviation safety systems demonstrated that commercial air travel continues to prioritize passenger welfare above all other considerations, maintaining its position as the safest mode of long-distance transportation available.

